
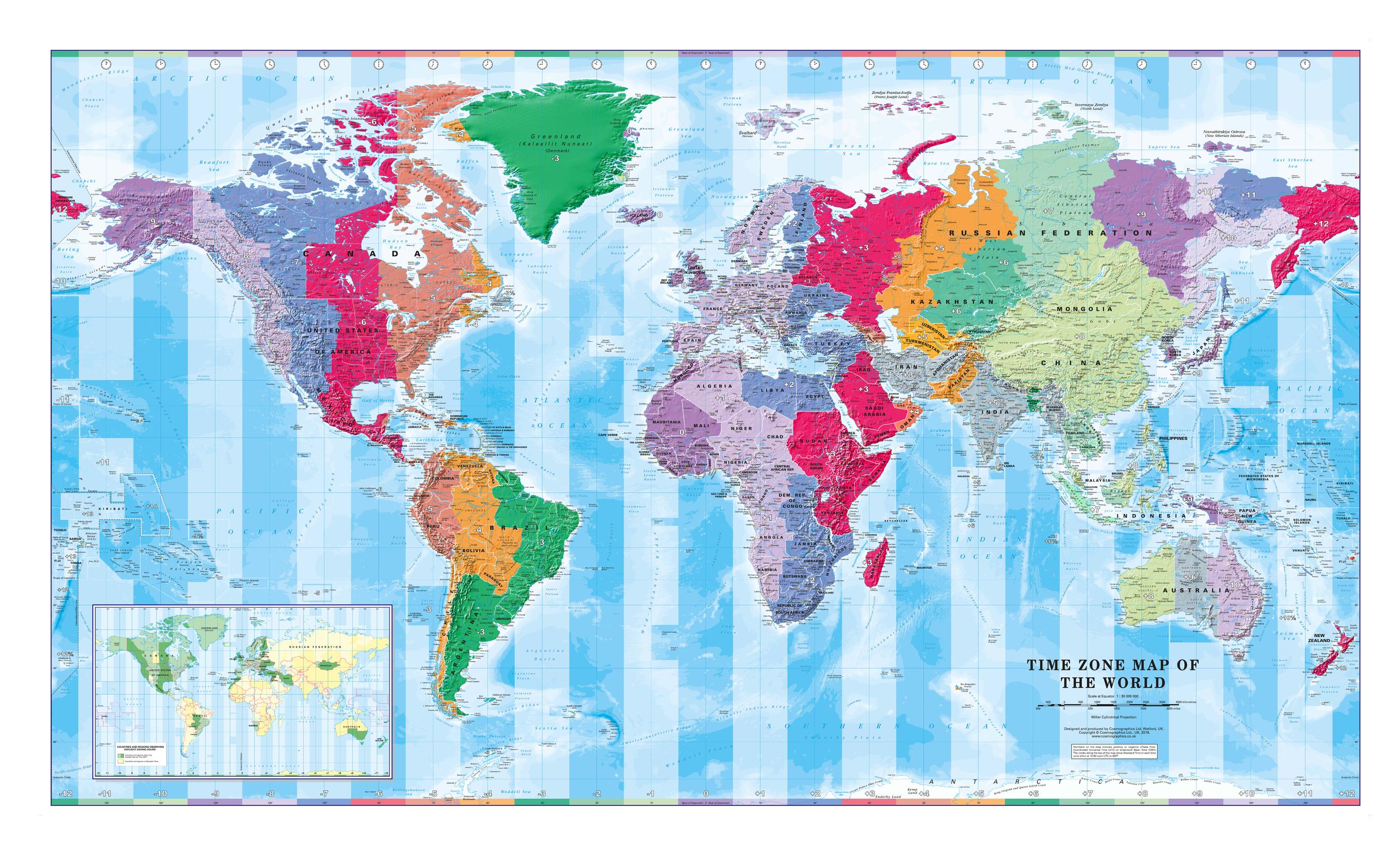
Fleming became a strong advocate of time zones to be usedįor all purposes. To reduce the remaining confusion at a union station, where all the lines converged, American Charles Ferdinand Dowd advocated geographic time zones for the railways. North American railways experimented with operatingĮach line on uniform time. England was the first country to adopt standardized time, with the railways forcing the issue. William Hyde Wollaston and Abraham Follett Osler promoted a system of universal time. Although many other travellers likely had similar experiences, Fleming’s personal experience seemed to inspire his search for a way of reducing confusion He became chief engineer for the Canadian Pacific Railway, Sir Sandford Fleming spent one uncomfortable night in a railway station due to the time confusion when changing trains. However, with the advent of railways, the multitude of municipal times became a significant aggravation for travellers. Everyone agreed on this arrangement when an 18 km journey was considered long, arduous, unpredictable or rare. For example, at a latitude of 49°, two municipalities would have differed in time by one minute for each 18 km of east-west separation, with the easternmost municipality having the Up to the 1880s, municipalities used their own local mean solar time. Sir Sandford Fleming and Greenwich Mean Time The official time reference for Canada comes from the National Research Council of Canada (NRC), but, except during wartime, the provinces and municipalities legislate the official time zone boundaries. Similarly, Saskatchewan follows CST year-round and, as of 2020, Yukon follows PDT, also known as Yukon Standard Time, year-round. Boundaries shift because some municipalities choose not to participate From the second Sunday in March to the first Sunday in November most of Canada follows daylight saving time.Ī portion of northeastern British Columbia in the summer, but not during the winter (see maps below). Referred to as standard time zones, and may be abbreviated as PST, MST, CST, etc. Similarly, Saskatchewan follows CST year-round and, as of 2020, Yukon follows PDT, also known as Yukon Standard Time, year-round.
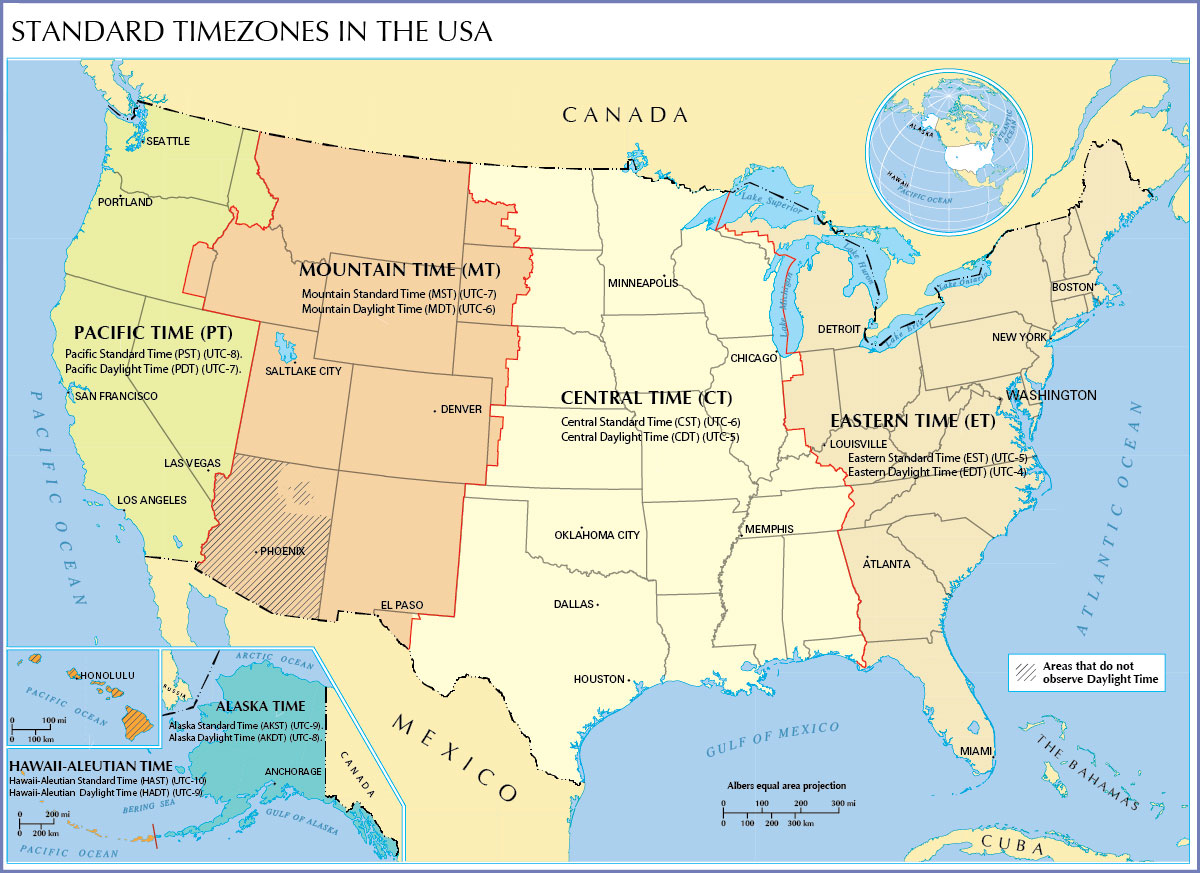
For example, the Mountain time zone includesĪ portion of northeastern British Columbia in the summer, but not during the winter (see maps below).
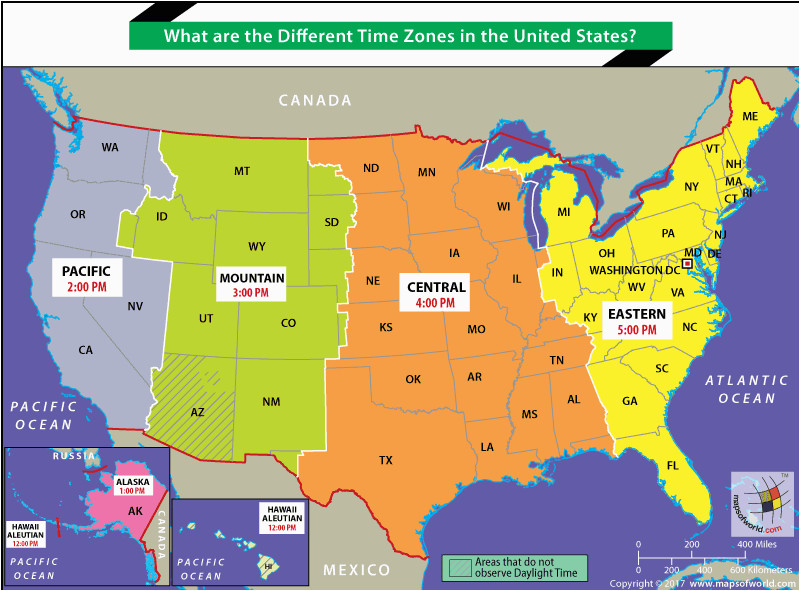
The boundaries of the standard time zones are not necessarily the same as those of the corresponding daylight saving time zones. From the second Sunday in March to the first Sunday in November most of Canada follows daylight saving time.ĭuring this summer period the time zones may be abbreviated as PDT, MDT, CDT, etc. From the first Sunday in November to the second Sunday in March these zones are From west to east these time zones are: Pacific, Mountain, Central, Eastern, Atlantic and Newfoundland. Since 2020 Yukon uses UTC-7h or Yukon Standard Time all year round.There are six time zones in Canada covering four and a half hours. Southampton Island remains on Eastern Standard time all year long. Nunavut covers 3 time zones and all zones change at 02:00 local time. Areas around Lloydminster are in the Mountain Time zone and change at 2:00 a.m. Most of Saskatchewan uses Central Standard time all year round. The areas of Ontario, west of 90° West longitude, are in the Central Time zone and change at 2:00 a.m. Return to first footnote 2 referrer Footnote 3

Some areas of Quebec east of 63° West longitude use Atlantic Time for all or part of the year. Prior to November 2011, Newfoundland changed time at 00:01 local time.
#MAP TIME ZONES SERIAL NUMBER#
(This has been denoted as serial number #07 as is transmitted in CHU code.) Province/Territory The time zone maps and the dates listed below have been in effect since 2020. Exceptions may exist in certain municipalities. When does daylight saving time start and end?ĭaylight saving time in Canada is determined by provincial legislation. These boundaries and changeover dates have serial number 07, broadcast in computer readable form on short wave station CHU along with Canada's official time reference UTC (NRC): Coordinated Universal Time, the modern implementation of Greenwich Time.Ī major change in official time practice will be given a new serial number and documented here. Starting in 2007, clocks following the new North American standard for Daylight Saving Time are to be turned forward by one hour on the second Sunday in March and turned back on the first Sunday of November. In Canada, Time Zones and Daylight Saving Time usually have been regulated by provincial and territorial governments. The times for the start and end of Daylight saving time in Canadian time zones can be found here.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
